Vitamin D3
Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol) Specification (USP)
| Appearance | White crystalline powder | Standard Packing | 500g/bag or per customer request | |
| Melting rang | 82° C -87° C | Inventory | Normally we have Vitamin D3 GMP certificated in stock | |
| 7-dehydrocholesterol | < 0.2% | |||
| Light absorption | 0.46-0.50 | Vitamin D3 physical parameters | ||
| Optical rotation | +105° ~ +112° | CAS No: | 67-97-0 | |
| Assay | ≥98% | Formula | C27H44O | |
| Specification | 40,000,000 IU/g | Molecular Weight | 384.64 | |
| Synonym | Cholecalciferol | |||
| Structure |
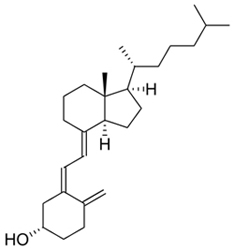 |
|||
|
What does vitamin D3 do? Vitamin D3 is necessary for the ultilization of Calcium and Phosphorus, and for the assimilation of Vitamin A. It also has a strong immune enhancing effect and controls blood pressure. Cautions: Anyone taking more than 1300 IU's per day should have periodic blood tests performed to be sure that not too much Calcium is being absorbed or that kidney and liver function is not adversely affected. Underlying kidney disease is a contraindication. High doses should be taken under the supervision of a physician. Dose of vitamin D3: Cancer patients should take 2000 to 3000 IU's per day on an empty stomach along with an essential fatty acid (see Flax oil, for example.) Everyone should get at least 15 to 30 minutes of sunshine directly on the skin at least 3 times per week. Adequate quantities of phytochemicals from vegetables and fruits, together with essential fatty acids, help prevent skin cancer, as does Vitamin D itself. More Detail Information about Vitamin D3: Cholecalciferol increases the serum calcium concentrations by: increasing GI absorption of phosphorus and calcium, increasing osteoclastic resorption, and increasing distal renal tubular reabsorption of calcium. Vitamin D3 is a naturally occurring bodily substance that many believe to exert a protective effect in multiple sclerosis - both in the development of the disease and in limiting its progression. D3 is best known for it's effects on calcium metabolism. Proper levels are necessary to maintain bone mineral density and serum (blood) calcium levels. This is especially true among the very young where it is used to treat rickets and in combination with vitamin A for the treatment of osteoporosis in the elderly, particularly post menopausal women who are often subject to fractures due to loss of bone density. Vitamin D3 can be produced photochemically by the action of sunlight or ultraviolet light from the precursor sterol 7-dehydrocholesterol which is present in the epidermis or skin of most higher animals. Cholecalciferol is transferred to the liver where it is converted to calcifediol (25-hydroxycholecalciferol), which is then transferred to the kidneys and converted to calcitriol (1,25-dihyroxycholecalciferol, thought to be the most active form) and 24,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. Cholecalciferol and ergocalciferol are hydroxylated in the liver by the enzyme vitamin D 25-hydroxylase to form 25-hydroxycholecalciferol (calcifediol) and 25-hydroxyergocalciferol respectively. These compounds undergo further hydroxylation in the kidneys by the enzyme vitamin D 1-hydroxylase to form the active metabolites 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol (calcitriol) and 1,25-dihydroxyergocalciferol respectively. Further metabolism also occurs in the kidneys, including the formation of the 1,24,25-trihydroxy derivatives. Of the synthetic analogues, alfacalcidol is converted rapidly in the liver to calcitriol, and dihydrotachysterol is hydroxylated, also in the liver, to its active form 25-hydroxydihydrotachysterol. Vitamin D3 is necessary for the ultilization of Calcium and Phosphorus, and for the assimilation of Vitamin A. It also has a strong immune enhancing effect and controls blood pressure. Vitamin D3 is the molecule responsible for calcium absorption from food and supplements into the bloodstream to be used throughout the body. Without sufficient levels of D3 in the blood, proper bone development and muscle contraction cannot take place. A Vitamin D3 deficiency will lead to serious medical conditions including malnutrition and metabolic bone disease. The latter may not show signs until a broken arm or leg occurs. Vitamin D3 is often thought to be the preferred vitamin because it has more biological activity. Vitamin D3 as found in food or in human skin always has various metabolites or isomers that may have biological benefit. There may be as many as 12 metabolites or isomers in the vitamin D found in animal foods. When vitamin D is taken in the form of fish oil, or eaten in foods such as eggs or fish, these metabolites will be present. Vitamin D3 is the active & preferable form of vitamin D. It is a fat soluble vitamin & its absorption depends upon the presence of bile & fats in the intestines. (If your gallbladder has been removed you will have no bile & may need to take one of our digestive aids containing ox bile). Vitamin D3 functions more like a hormone than a vitamin because of the many cellular functions it affects. Many investigators already regard vitamin D as a hormone because of its sterol chemical structure & the fact that sunlight on your skin can use your body to make vitamin D. |
||||
| Certificate of Analysis | Vitamin D3 COA | |||
| Literature | Vitamin D3 literature | |||
| MSDS | Vitamin D3 MSDS | |||
| References: | ||||
| 1. | ||||
| 2. | ||||
| . | ||||
|
Copyright © 2020 - . All Rights Reserved |
||||